JohnThurlow.com
COMPLEX THINKING
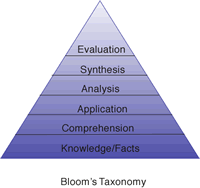
Benjamin Bloom (1956) developed a classification of levels of intellectual behavior in learning. This taxonomy contained three overlapping domains: the cognitive, psychomotor, and affective. Within the cognitive domain, he identified six levels: knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. These domains and levels are still useful today as we help develop the critical thinking skills of our students.
Taxonomy of Thinking Skills
(adapted from Bloom's Taxonomy of Thinking Skills)
| Category |
Knowledge
Information Gathering |
Comprehension
Confirming |
Application
Making Use of Knowledge
|
Analysis
(Higher Order)
Taking Apart
|
Synthesis
(Higher Order)
Putting Together
|
Evaluation
(Higher Order)
Judging the Outcome
|
Description
The skills demonstrated at this level are those of: |
- observation and recall of information;
- knowledge of dates, events, places;
- knowledge of major ideas;
- mastery of subject matter.
|
- understanding information;
- grasping meaning;
- translating knowledge into new context;
- interpreting facts, comparing, contrasting;
- ordering, grouping, inferring causes;
- predicting consequences.
|
- using information;
- using methods; - concepts, theories in new situations;
- solving problems using required skills or knowledge.
|
- seeing patterns;
- organization of parts;
- recognition of hidden meanings;
- identification of components.
|
- using old ideas to create new ones;
- generalizing from given facts;
- relating knowledge from several areas;
- predicting, drawing conclusions.
|
- comparing and discriminating between ideas;
- assessing value of theories, presentations;
- making choices based on reasoned argument;
- verifying value of evidence;
- recognizing subjectivity.
|
What the Student Does
|
Student recalls or recognizes information, ideas, and principles in the approximate form in which they were learned. |
Student translates, comprehends, or interprets information based on prior learning. |
Student selects, transfers, and uses data and principles to complete a problem or task. |
Student distinguishes, classifies, and relates the assumptions, hypotheses, evidence, or structure of a statement or question. |
Student originates, integrates, and combines ideas into a product, plan or proposal that is new to him or her. |
Student appraises, assesses, or critiques on a basis of specific standards and criteria. |
Sample Trigger Words
|
- define
- list
- label
- name
- identify
- repeat
- who
- what
- when
- where
- tell
- describe
- collect
- examine
- tabulate
- quote
|
- predict
- associate
- estimate
- differentiate
- summarize
- describe
- interpret
- discuss
- extend
- compare
- contrast
- distinguish
- explain
- paraphrase
- illustrate
|
- apply
- demonstrate
- complete
- illustrate
- show
- examine
- modify
- relate
- change
- classify
- experiment
- discover
- use
- compute
- solve
- construct
- calculate
|
- separate
- order
- explain
- connect
- divide
- compare
- select
- explain
- infer
- arrange
- classify
- analyze
- categorize
- compare
- contrast
- separate
|
- combine
- integrate
- rearrange
- substitute
- plan
- create
- design
- invent
- what it?
- Prepare
- generalize
- compose
- modify
- create
- design
- hypothesize
- invent
- develop
- formulate
- rewrite
|
- decide
- grade
- test
- measure
- recommend
- judge
- explain
- compare
- summarize
- assess
- judge
- recommend
- critique
- justify
- discriminate
- support
- convince
- conclude
- select
- rank
- predict
- argue
|
| Category |
Knowledge
Information Gathering |
Comprehension
Confirming |
Application
Making Use of Knowledge
|
Analysis
(Higher Order)
Taking Apart
|
Synthesis
(Higher Order)
Putting Together
|
Evaluation
(Higher Order)
Judging the Outcome
|
Sample Task(s)
|
Name the food groups and at least two items of food in each group.
Make an acrostic poem about healthy food. |
Write a simple menu for breakfast, lunch or dinner using the food guide chart. |
What would you ask shoppers in a supermarket if you were doing a survey of what food they eat? (10 questions)
|
Prepare a report about what the people in this class eat for breakfast. |
Create a song and dance to sell bananas. |
Make a booklet about 10 important eating habits that would be suitable for the whole school to follow in order to eat correctly. |
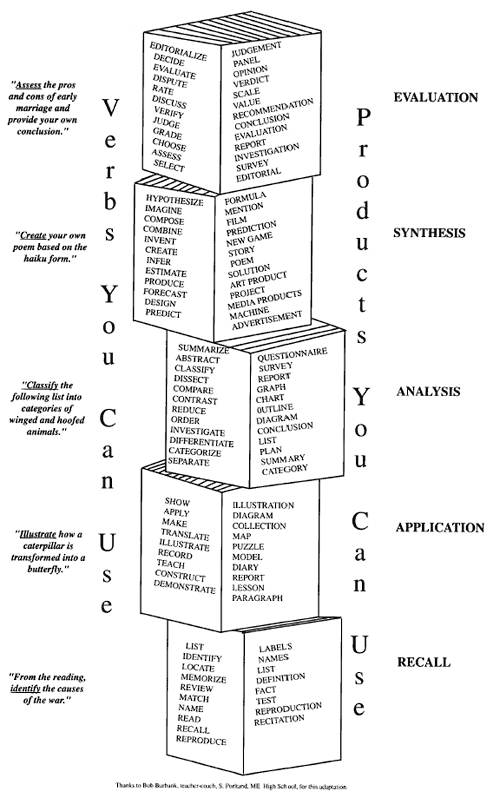
Bloom's Taxonomy and Critical Thinking
Bloom's Taxonomy divides the way people learn into three domains. One of these is the Cognitive Domain which emphasizes intellectual outcomes. This domain is further divided into categories or levels. The key words used and the type of questions asked may aid in the establishment and encouragement of critical thinking, especially in the higher levels.
The other two domains are the Affective Domain which includes interpersonal relations, emotions, attitudes, appreciations, and values: Keywords defining the domain are: accepts, attempts, challenges, judges, defends, disputes, joins, contributes, praises, questions, shares, supports, volunteers
- The Psychomotor Domain's attributes are fine and gross motor skills such as: bend, grasp, handle, kick, operate, reach, relax, stretch, type, write, express, perform, conduct, act.
-
COGNTIVE DOMAIN
Level 1: Knowledge - exhibits previously learned material by recalling facts, terms, basic concepts and answers.
Key words: who, what, why, when, omit, where, which, choose, find, how, define, label, show, spell, list, match, name, relate, tell, recall, select
Questions:
What is . . . ? How is . . . ?
Where is . . . ? When did _______ happen?
How did ______ happen? How would you explain . . . ?
Why did . . . ? How would you describe . . . ?
When did . . . ? Can you recall . . . ?
How would you show . . . ? Can you select . . . ?
Who were the main . . . ? Can you list three . . . ?
Which one . . . ? Who was . . . ?
Level 2: Comprehension - demonstrating understanding of facts and ideas by organizing, comparing, translating, interpreting, giving descriptions and stating main ideas.
Key words: compare, contrast, demonstrate, interpret, explain, extend, illustrate, infer, outline, relate, rephrase, translate, summarize, show, classify
Questions:
How would you classify the type of . . . ?
How would you compare . . . ? contrast . . . ?
Will you state or interpret in your own words . . . ?
How would you rephrase the meaning . . . ?
What facts or ideas show . . . ?
What is the main idea of . . . ?
Which statements support . . . ?
Can you explain what is happening . . . what is meant . . .?
What can you say about . . . ?
Which is the best answer . . . ?
How would you summarize . . . ?
Level 3: Application - solving problems by applying acquired knowledge, facts, techniques and rules in a different way.
Key words: apply, build, choose, construct, develop, interview, make use of, organize, experiment with, plan, select, solve, utilize, model, identify
Questions:
How would you use . . . ?
What examples can you find to . . . ?
How would you solve _______ using what you have learned . . . ?
How would you organize _______ to show . . . ?
How would you show your understanding of . . . ?
What approach would you use to . . . ?
How would you apply what you learned to develop . . . ?
What other way would you plan to . . . ?
What would result if . . . ?
Can you make use of the facts to . . . ?
What elements would you choose to change . . . ?
What facts would you select to show . . . ?
What questions would you ask in an interview with . . . ?
Level 4: Analysis - examining and breaking information into parts by identifying motives or causes; making inferences and finding evidence to support generalizations.
Key words: analyze, categorize, classify, compare, contrast, discover, dissect, divide, examine, inspect, simplify, survey, take part in, test for, distinguish, list, distinction, theme, relationships, function, motive, inference, assumption, conclusion
Questions:
What are the parts or features of . . . ?
How is _______ related to . . . ?
Why do you think . . . ?
What is the theme . . . ?
What motive is there . . . ?
Can you list the parts . . . ?
What inference can you make . . . ?
What conclusions can you draw . . . ?
How would you classify . . . ?
How would you categorize . . . ?
Can you identify the difference parts . . . ?
What evidence can you find . . . ?
What is the relationship between . . . ?
Can you make a distinction between . . . ?
What is the function of . . . ?
What ideas justify . . . ?
Level 5: Synthesis - compiling information together in a different way by combining elements in a new pattern or proposing alternative solutions.
Key Words: build, choose, combine, compile, compose, construct, create, design, develop, estimate, formulate, imagine, invent, make up, originate, plan, predict, propose, solve, solution, suppose, discuss, modify, change, original, improve, adapt, minimize, maximize, delete, theorize, elaborate, test, improve, happen, change
Questions:
What changes would you make to solve . . . ?
How would you improve . . . ?
What would happen if . . . ?
Can you elaborate on the reason . . . ?
Can you propose an alternative . . . ?
Can you invent . . . ?
How would you adapt ________ to create a different . . . ?
How could you change (modify) the plot (plan) . . . ?
What could be done to minimize (maximize) . . . ?
What way would you design . . . ?
What could be combined to improve (change) . . . ?
Suppose you could _______ what would you do . . . ?
How would you test . . . ?
Can you formulate a theory for . . . ?
Can you predict the outcome if . . . ?
How would you estimate the results for . . . ?
What facts can you compile . . . ?
Can you construct a model that would change . . . ?
Can you think of an original way for the . . . ?
Level 6: Evaluation - presenting and defending opinions by making judgments about information, validity of ideas or quality of work based on a set of criteria.
Key Words: award, choose, conclude, criticize, decide, defend, determine, dispute, evaluate, judge, justify, measure, compare, mark, rate, recommend, rule on, select, agree, interpret, explain, appraise, prioritize, opinion, ,support, importance, criteria, prove, disprove, assess, influence, perceive, value, estimate, influence, deduct
Questions:
Do you agree with the actions . . . ? with the outcomes . . . ?
What is your opinion of . . . ?
How would you prove . . . ? disprove . . . ?
Can you assess the value or importance of . . . ?
Would it be better if . . . ?
Why did they (the character) choose . . . ?
What would you recommend . . . ?
How would you rate the . . . ?
What would you cite to defend the actions . . . ?
How would you evaluate . . . ?
How could you determine . . . ?
What choice would you have made . . . ?
What would you select . . . ?
How would you prioritize . . . ?
What judgment would you make about . . . ?
Based on what you know, how would you explain . . . ?
What information would you use to support the view . . . ?
How would you justify . . . ?
What data was used to make the conclusion . . . ?
Why was it better that . . . ?
How would you prioritize the facts . . . ?
How would you compare the ideas . . . ? people . . . ?
Copyright © 1996
Critical Thinking Across the Curriculum Project
Longview Community College , Lee's Summit, Missouri - U.S.A.
One of the Metropolitan Community Colleges
An Equal Opportunity/Affirmative Action Employer
Permission to reproduce these resource pages is granted for
non-profit educational use provided the above information
is retained on all copies.

